
How do you build AI apps right now?
Langchain recently crossed 200 million monthly Python package downloads, and one-third of the Fortune 500 now uses it.
They also launched Agent Builder, their no-code agent platform.
It started as an 800-line side project by Harrison Chase in October 2022, and now it's the default framework for building AI apps that go beyond a single API call.
But the ecosystem has gotten large enough that figuring out what matters vs what's noise is its own problem.
So I went through the docs, the codebase, and built a working app with it. But before that:
Dev Tools of the Week
1. Unblocked
AI code review that understands your codebase, integrates with GitHub/GitLab, learns from your team's patterns, and catches issues before they hit production.
2. Tines
No-code automation for security and IT workflows. Think Zapier but built for technical teams handling incident response, threat detection, and compliance tasks.
3. npmx.dev
Command runner that lets you execute any npm package directly without installation. Run npx commands from any package registry instantly.
What is langchain?
Every AI provider has different APIs, message formats, and response structures.
LangChain wraps them in one interface.
You can swap between them by changing one line:
The ecosystem: main langchain package, provider-specific packages, LangGraph for orchestration, LangSmith for debugging, and Deep Agents for autonomous tasks.
The build: PDF chatbot with RAG
Goal is to upload a PDF, ask questions, and get answers grounded in the actual document.
This uses RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation).
A question comes in → system searches the document → relevant sections get passed to the model → model answers from that context instead of guessing.
Step 1: Install

store your API key in a .env file and add it to .gitignore.
Step 2: Load and split
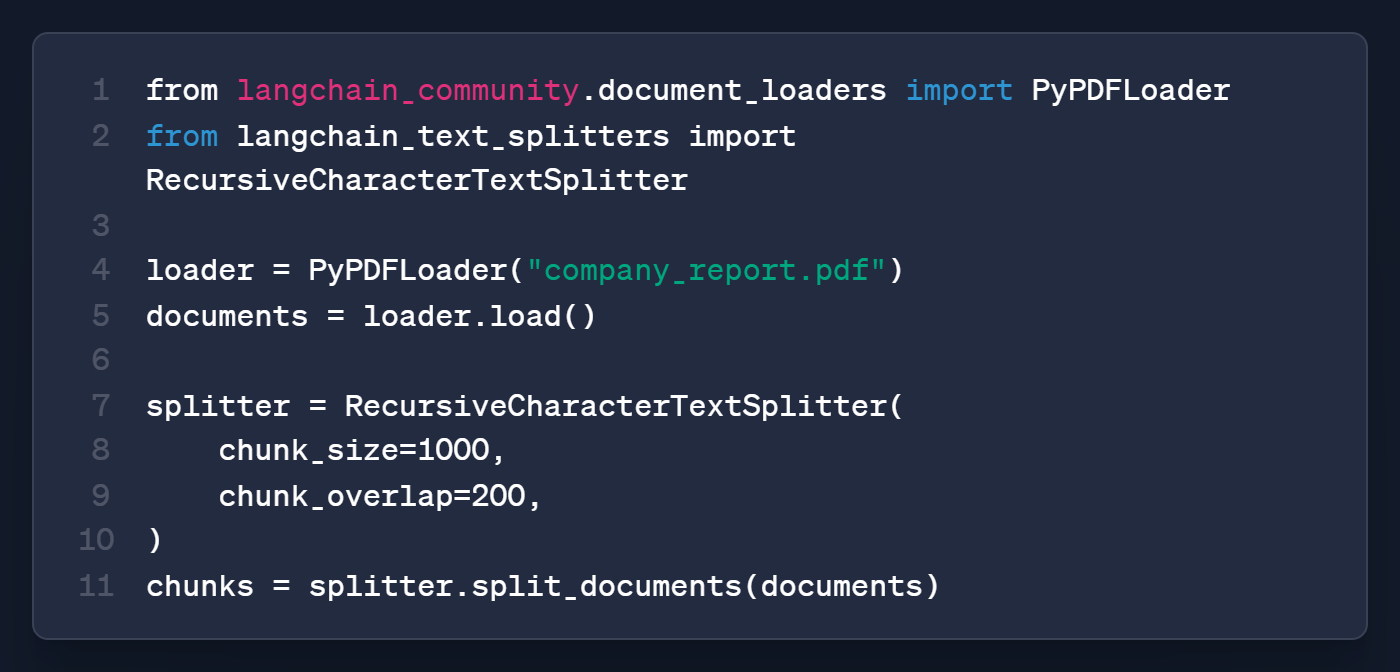
The splitter breaks pages into smaller pieces. First paragraphs, then sentences only when necessary.
Smaller chunks mean more precise search results.
The overlap prevents info at boundaries from getting cut mid-thought.
Chunk_size is the tuning knob you'll spend the most time on.
Too small (300), and you get fragments without context; too large (3000), and noise buries the signal.
1000/200 works for most documents; adjust from there based on what your retriever returns.
Step 3: Embed and store
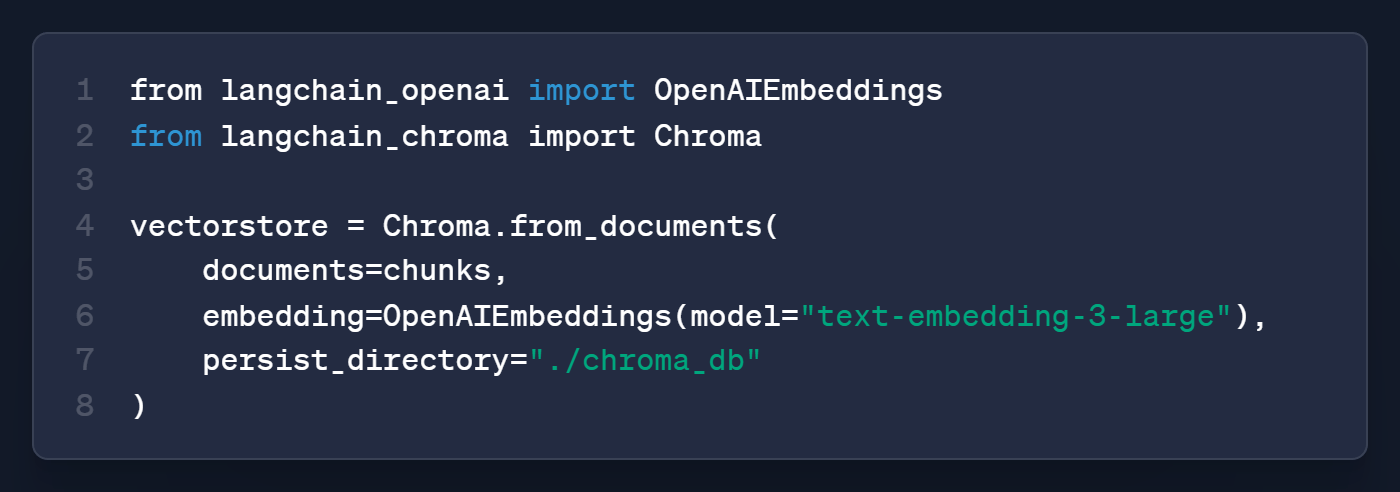
Each chunk becomes a vector, a list of numbers representing meaning.
"What was revenue?" and "How much money did they make?" get similar vectors even though they share no words.
Semantic search runs on this instead of keyword matching.
Step 4: Build the chain

This is LangChain's pipe syntax. Every component is a runnable, and | connects them.
The dictionary runs two things in parallel.
The question passes through unchanged; context sends the question to the retriever, which returns the 4 most relevant chunks.
Both feed into the prompt, model answers, and the parser extracts text.
The system prompt instruction "if the context doesn't contain the answer, say so" prevents hallucination.
Without it, the model fills gaps with invented information.
Step 5: Use it

The chain searches the PDF, finds relevant sections, answers from them.
Ask the same model the same question without a document context, and it either admits ignorance or invents a number.
Stream it token by token:

Add memory
Right now every question is independent.
"What was the revenue?" then "How does that compare to last year?" and the chain has no idea what "that" refers to.

MessagesPlaceholder creates a slot for previous messages in the prompt. The model now sees the full conversation context.
if you see ConversationBufferMemory in a tutorial, it's outdated. Those classes were deprecated in favour of direct message management and LangGraph persistence.
Add an agent (only if you need one)
The RAG chain always retrieves, even for "what is 2+2?", which is wasteful.
An agent decides whether to search or just answer:
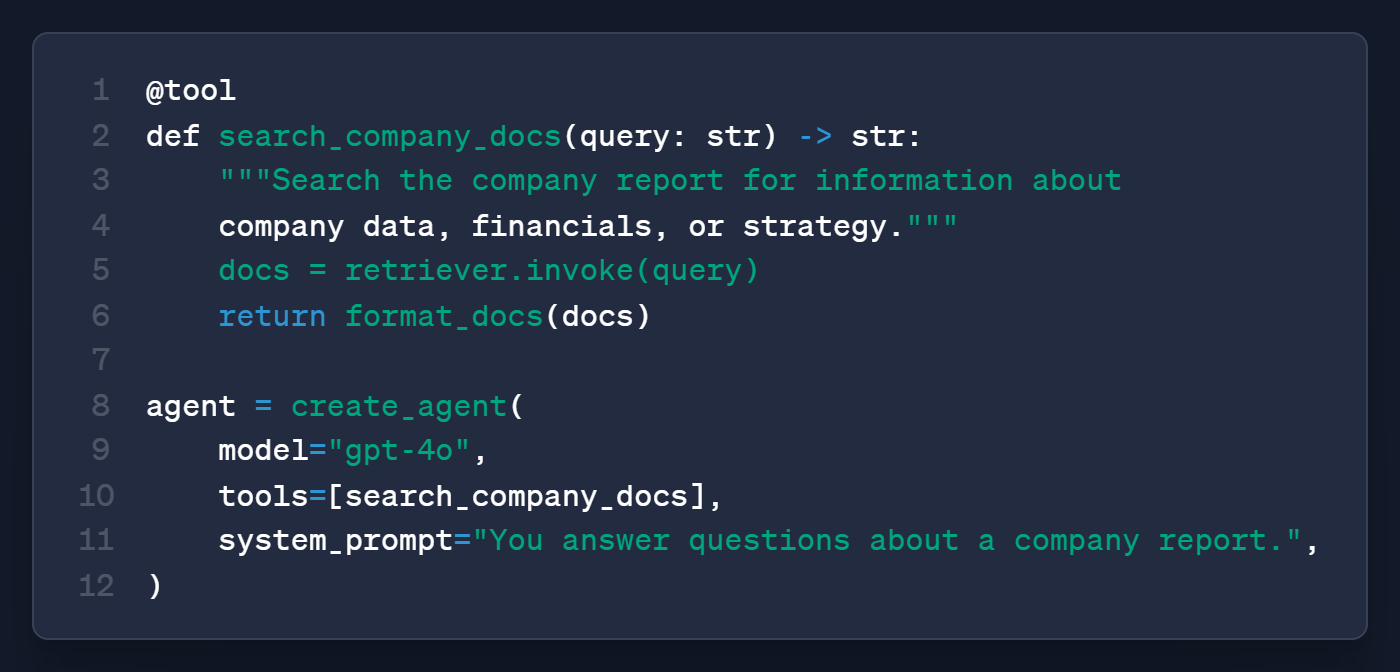
The agent looks at the question, decides if it needs the document, and acts accordingly, ask "what is 2+2?" and it skips the tool entirely.
Use this over the chain only when you have multiple tools or the model needs to decide between actions.
For single-document Q&A, the chain is simpler and more reliable.
Production basics
Caching: the same question twice = instant, free. InMemoryCache for testing, SQLiteCache for persistence.
Fallbacks: When the primary model goes down, automatic switch to backup. Double as a cost strategy by trying the cheap model first.
Tracing: enable LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2=true with LangSmith for a visual trace of every step. essential when debugging retriever issues.
Mistakes to avoid

My take
LangChain makes the first 80% of building an AI app easy.
Provider swapping, RAG, memory, and tool use are all handled.
The last 20% is where it gets frustrating.
When the retriever returns wrong chunks or the agent loops on a hallucinated tool call, you get sucked into debugging LangChain's abstractions.
The framework that saves you time on day one costs you time on day thirty when something breaks and the abstraction layer sits between you and the fix.
I'd still use it for any project that involves retrieval, tools, or multi-step chains.
The alternative is worse, but go in knowing you'll eventually need to understand what's happening underneath.
Build the PDF chatbot this week, swap in your own document reply and tell me what you're building with it.
Until next time,
Vaibhav 🤝🏻
If you read till here, these might be interesting:
#AD1
Meet America’s Newest $1B Unicorn
It just surpassed a $1B valuation, joining private US companies like SpaceX and OpenAI. Unlike those companies, you can invest in EnergyX today. Industry giants like General Motors and POSCO already have. Why? EnergyX’s tech can recover 3X more lithium than traditional methods. Now, they’re preparing 100,000+ acres of lithium-rich Chilean land for commercial production. Buy private EnergyX shares alongside 40k+ people at $11/share through 2/26.
This is a paid advertisement for EnergyX Regulation A offering. Please read the offering circular at invest.energyx.com. Under Regulation A, a company may change its share price by up to 20% without requalifying the offering with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
#AD2
AI is all the rage, but are you using it to your advantage?
Successful AI transformation starts with deeply understanding your organization’s most critical use cases. We recommend this practical guide from You.com that walks through a proven framework to identify, prioritize, and document high-value AI opportunities. Learn more with this AI Use Case Discovery Guide.





